In vitro and in vivo studies to understand WFs pathogenesis were selected. Welding fumes have been classified as carcinogenic to humans Group 1 by the International Agency for Research on Cancer IARC.

Pdf Welding Fumes A Risk Factor For Lung Diseases Semantic Scholar
In vitro and in vivo studies to understand WFs pathogenesis were.

Welding fumes a risk factor for lung diseases. Our results showed that welding fumes CrVI and Ni may contribute independently to the excess lung cancer risk associated with welding. Most research has found a relationship between welding fume exposure and lung decline but other studies have shown no relationship. The state of current research leaves several gaps in.
In this population occupational exposure to welding fumes accounted for approximately 4 of lung cancer cases to which both stainless and mild steel welding contributed equally. The respiratory issues seen most with overexposure are. Welding fumes WFs are composed of fine and ultrafine particles which may reach the distal airways and represent a risk factor for respiratory diseases.
However quantitative exposure assessment remains. In vitro and in vivo studies to understand WFs pathogenesis were selected. Stainless steel welding fumes contain high levels of nickel and chromium VI compounds which are established human lung carcinogens.
1011 Inhalational changes as a result of welding fume exposure were. 8 9 The inhalation of the welding fumes also expose welders to increased risk of pneumonic infections as well as lung cancer. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD.
Contemporary epidemiological evidence points to an increased lung cancer risk particularly among stainless steel welders. Given that welding remains a common task for many workers exposure to welding fumes represents an important risk factor for lung cancer. The study Welding Fumes A Risk Factor for Lung Diseases explores the types of lung damage that can occur from overexposure to welding fumes from both gases and metals.
12 Chronic exposure to metal fumes blunts the inflammatory response of lung tissue against inhaled particulate matter which may predispose to the development of respiratory infection. There is agreement that welding increases the risk of chronic productive cough pneumonia and lung cancer and may cause occupational asthma. Further studies in the area of particle research may aid the understanding of mechanisms involved in welding-related lung disease and to expand knowledge in welding-related cardiovascular diseases.
Several meta-analyses have indicated that exposure to welding fumes of any type increases the risk of lung cancer 120121122123124 125. Current research has reported conflicting data related to welding fume exposure and lung decline. Welding fumes WFs are composed of fine and ultrafine particles which may reach the distal airways and represent a risk factor for respiratory diseases.
Welding fumes WFs are composed of fine and ultrafine particles which may reach the distal airways and represent a risk factor for respiratory diseases. The eligible risk factor will be occupational exposure to welding fumes measured directly or indirectly ie through proxy of relevant occupation work task job-exposure matrix expert judgment or self-report. Welding Fumes a Risk Factor for Lung Diseases.
Welding fumes WFs are composed of fine and ultrafine particles which may reach the distal airways and represent a risk factor for respiratory diseases. Reduced Cross-Shift Lung Function and Respiratory Symptoms among Integrated Textile Factory Workers in Ethiopia. Several studies have corroborated the excess risk among stainless steel welders.
The eligible outcomes will be trachea bronchus and lung cancer. 13 Specifically chromium is most likely the primary constituent responsible for suppression of lung. Among the regular welders welding was associated with a risk of lung cancer OR17 95 CI 11 to 25 which increased with the duration OR20 95 CI 10 to 39 when duration 10.
In the SYNERGY meta-analysis the overall odds. Animal studies have demonstrated that exposure to stainless steel welding fumes which contain large amounts of chromium and nickel promotes lung inflammation and injury. This assessment found sufficient evidence from studies in humans that welding fumes are a cause of lung cancer.

Pdf Welding Fumes A Risk Factor For Lung Diseases Semantic Scholar

Pdf Welding Fumes A Risk Factor For Lung Diseases Semantic Scholar
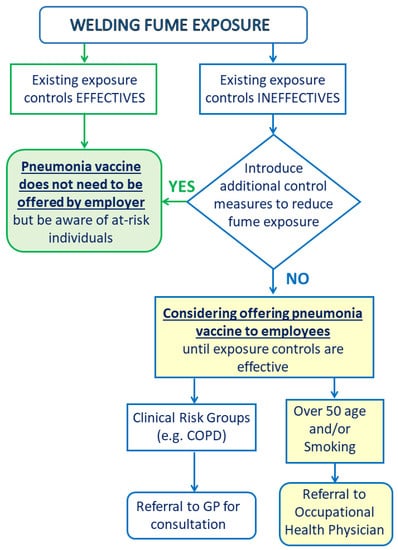
Ijerph Free Full Text Welding Fumes A Risk Factor For Lung Diseases Html
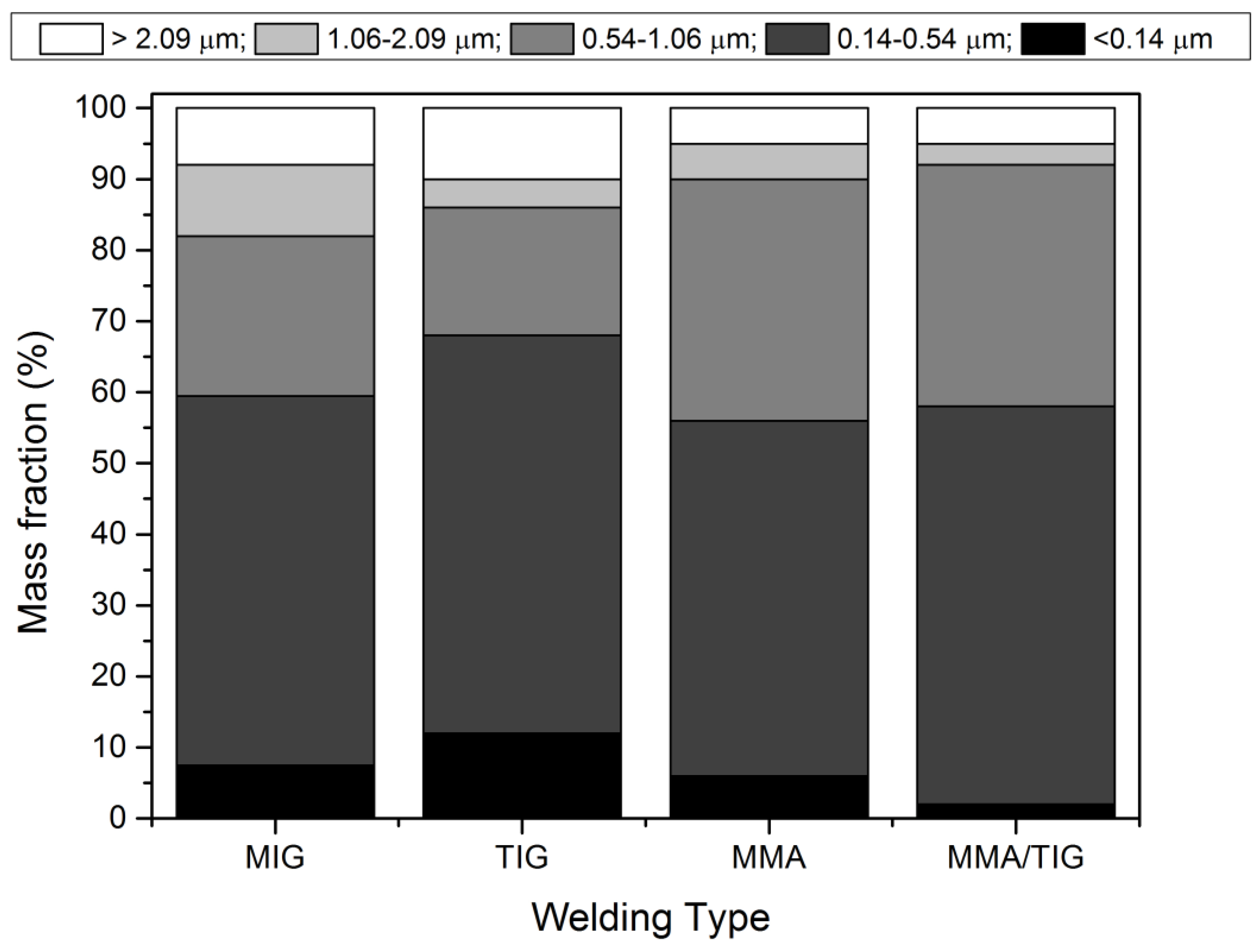
Ijerph Free Full Text Welding Fumes A Risk Factor For Lung Diseases Html

Pdf Welding Fumes A Risk Factor For Lung Diseases Semantic Scholar
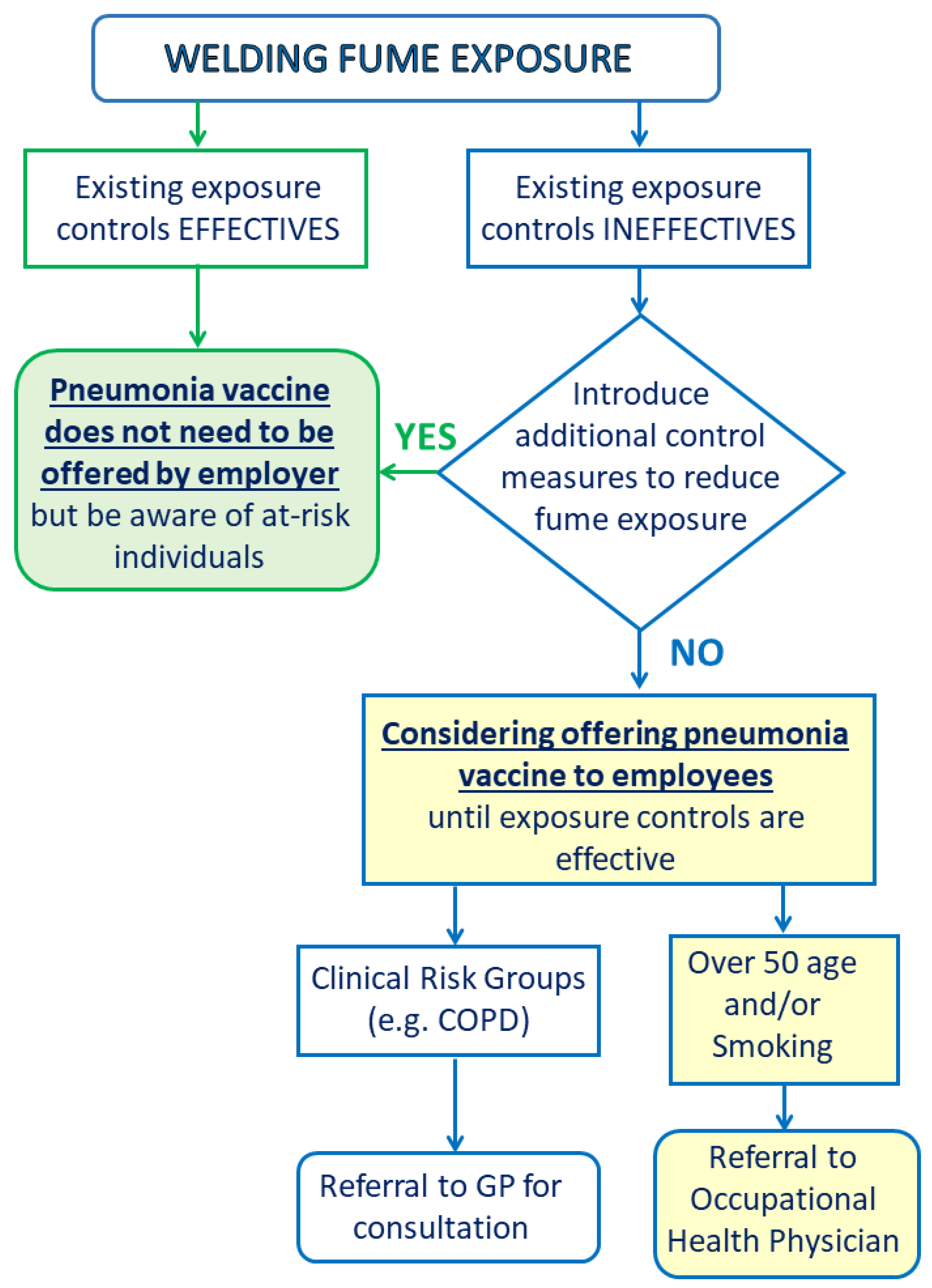
Ijerph Free Full Text Welding Fumes A Risk Factor For Lung Diseases Html

Pdf Welding Fumes A Risk Factor For Lung Diseases Semantic Scholar

Pdf Welding Fumes A Risk Factor For Lung Diseases Semantic Scholar

0 comments:
Post a Comment